“Cognitive focus theory” explains “luck” in terms of human relationships with time
Do you consider yourself “lucky”?
Even if you don’t rely on luck, you may sometimes buy a lottery ticket or somehow find good luck. There are various people in Japan and overseas who are attempting to research this kind of “luck.”
In this article, we will introduce theories and research related to luck, such as cognitive focus theory, achievement, and “Which is more important for success? Talent?”
“Cognitive focus theory” explains “luck” in terms of human relationships and time axis
The person developing the cognitive focusing theory is Satoshi Fujii, a professor at Kyoto University’s Graduate School of Engineering, who also served as a Cabinet Secretariat advisor in the second Abe cabinet. Many of you may have seen this on TV.
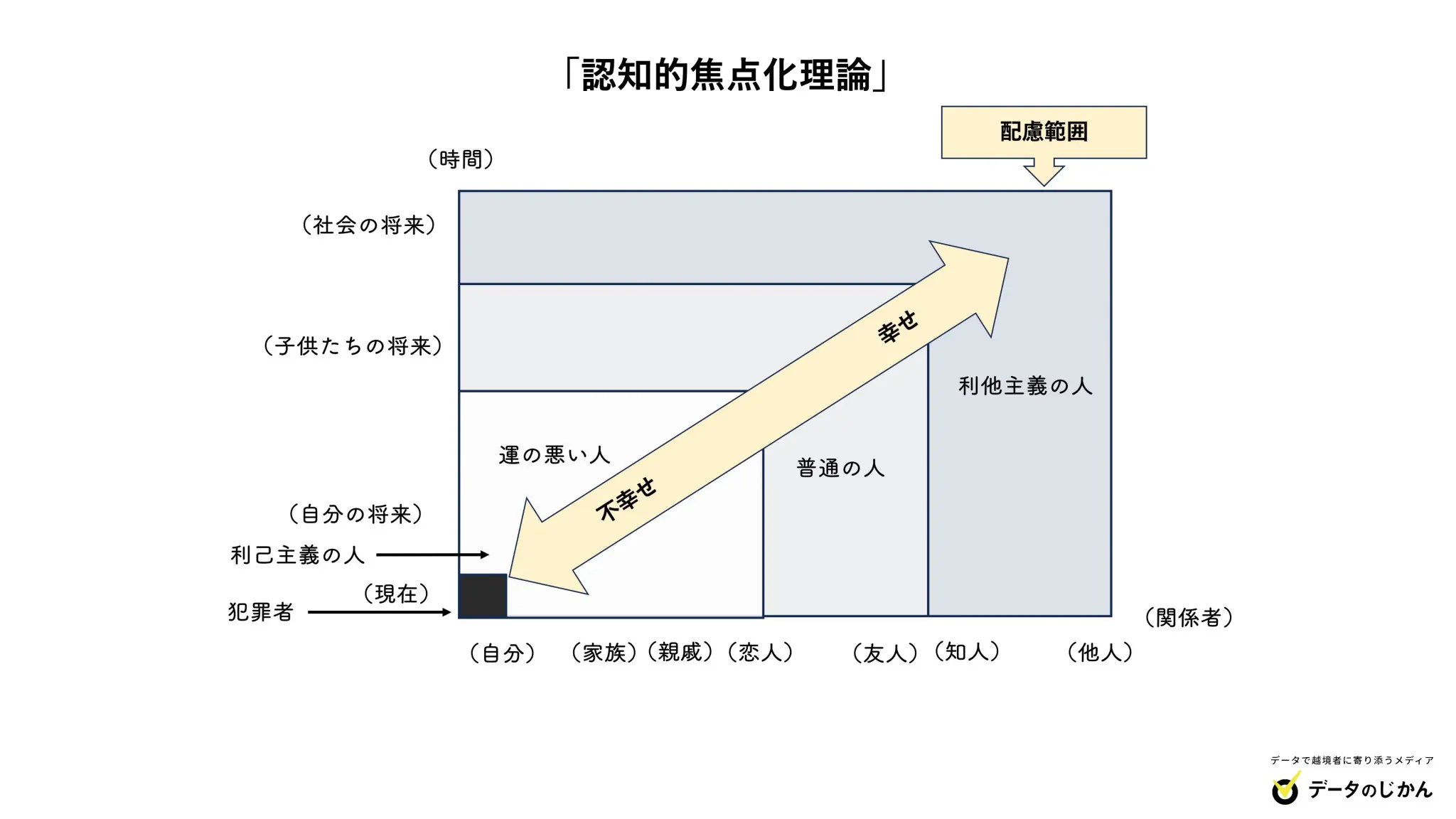
In a nutshell, the key points of the theory are: “The area of ”human relationships” and “time axis” that a person perceives determines whether that person gains or loses (≒ good luck or bad luck). ” is a psychological study.
According to Fujii, the lucky ones are those who have a wide range of human relationships that they are aware of, and whose time horizons also extend to the future vision of society. I tend to think that people who behave selfishly and monopolize profits will ultimately benefit, but due to the three principles that exist in human society: the principle of non-reciprocity, the principle of exposure, and the principle of collective selection , it is possible to calculate profits and losses. Mr. Fujii explains that people who act selfishly end up losing money.
Speaking of research on how humans behave selfishly, the article below covers spiking behavior (a “teasing” behavioral strategy that prevents others from gaining even at the cost of one’s own loss).
Spite behavior aims at a loss-lose outcome for both yourself and the other person. For a time, you may feel less satisfied because you didn’t lose to the opponent in front of you, but if you focus on your surroundings and the future according to cognitive focusing theory, you will still sometimes be able to hand over benefits to the other person. Ultimately , it would be ideal to aim for a win-win situation for both parties.
When you find yourself on the verge of engaging in “spiking behavior”, it may be helpful to remember the cognitive focusing theory.
Wearable sensors reveal the relationship between “achievement level” and luck
Next, I would like to introduce a book written by Kazuo Yano of Hitachi, Ltd., who researches “human happiness” using wearable sensors and big data. The invisible hand of data: the laws of humans, organizations, and society revealed by wearable sensorsIt is a theory of luck that uses an index called “degree of achievement” described in “Achievement” (Kusashisha, 2014).
“Achievement level” is a numerical expression of the “possibility of meeting people through connections with others.” For example, if you have 5 people you know, and each person has 3 indirect acquaintances, your reach is 5 times 3, which is 15 (assuming each acquaintance doesn’t know each other). .
Mr. Yano’s team, in collaboration with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), had about 30 employees on an inquiry response team wear wearable sensors to see if their responses were successful (on average, how well did they respond to complex quotation requests). We have obtained some knowledge regarding the relationship between the ability to answer questions in a short amount of time and achievement level.
The idea is that “people with higher reachability are better able to handle inquiries . “
What I would like to focus on here is that rather than simply having a large number of acquaintances, it was “a high level of reach, including networks of “acquaintances” and “acquaintances of acquaintances”” that led to success in work.
Are there people around you who seem to be able to complete difficult tasks with the help of others (= lucky)?
Such people may actually record high scores in “achievement.” If so, there is one way you can improve your luck.
“Build a relationship with that person who has a high level of attainment and raise your own level of attainment. “
Winner of the Ig Nobel Prize in Economics 2022! Research simulating “talent vs. luck”
The last thing I would like to discuss is the Ig Nobel Prize, which is given to research that makes people laugh and think, and the 2022 winner of the economics category,TALENT VERSUS LUCK: “THE ROLE OF RANDOMNESS IN SUCCESS AND FAILURE” is.
As of 2021, the top 10% own about 76% of the wealth, and the bottom 50% only get about 2%. The paper’s preface asks, “Even if there are differences in talent between individuals, will there be a 1,000-fold or 10,000-fold difference?”
An attempt was made to build a simulation model in which 1,000 virtual individuals live, each with a different talent value, and to have lucky/unfortunate events randomly occur every six months (on a virtual time axis). This is an experiment in which a simulation is repeated for 40 years to generate capital and give capital/success accordingly. The simulation started with talent values distributed according to a normal distribution, where talent values were tied to the probability of doubling or halving capital/success.
the distribution of capital/success has become a very skewed mirror of reality … Even though talent values were distributed according to a normal distribution.
And the most successful individuals were also the ones with the most luck, having a talent value of 0.61, just slightly more than the average of 0.6. Overall, it is clear that luck is more correlated with capital/success than talent.
This study, which uses data to reveal a cruel system in which luck determines a large part of success, resonated with many on social media. Although details such as the definition of talent may be up for debate, this far-fetched conclusion certainly rings true.
At the end We introduced three studies and theories about “luck,” which is often thought to be in the opposite position from words such as experiment and theory.
Whether you can control your luck or not depends on your definition and the scope of “luck” . Even though it is impossible to acquire a handful of wealth without innate luck, it seems that the luck needed to proceed smoothly in today’s work can be improved based on cognitive focusing theory and attainment.
Let’s face our luck with the attitude of “doing our best and waiting for destiny!”
[Reference materials]
- Satoshi Fujii “Revealed! Why are unlucky people unlucky?” 藤井聡『解明! 運がない人はなぜ運がないのか』┃President Online
- WORLD INEQUALITY REPORT 2022
- Kazuo YanoThe invisible hand of data: the laws of humans, organizations, and society revealed by wearable sensors” Soshisha 矢野和男『データの見えざる手 ウエアラブルセンサが明かす人間・組織・社会の法則』草思社, 2014
- Alessandro Pluchino, Alessio Emanuele Biondo, and Andrea Rapisarda, for explaining, mathematically,why success most often goes not to the most talented people, but instead to the luckiest.(“Talent vs. Luck: The Role of Randomness in Success and Failure,” Alessandro Pluchino, Alessio Emanuele Biondo, and Andrea Rapisarda, Advances in Complex Systems, vol. 21, nos. 3 and 4, 2018)